The Different Types of Sales | A Quick Guide
- May 13, 2024
- 19 mins read
- Listen

Table of Content
Imagine this: you walk into your favorite store, greeted by friendly faces and enticing displays. As you browse, you are subtly guided towards certain products, tempted by irresistible deals and recommendations tailored just for you. Meanwhile, in the digital world, algorithms work tirelessly to predict your next purchase before you even realize you want it. Different types of sales, in all its forms, surround us in our daily lives, shaping our shopping experiences in ways we may not always notice.
At first glance, selling seems simple: someone buys from someone else. But it’s more than just a transaction. It’s a journey from being interested in something to buying it. This journey can be complicated and needs a personal touch to finish it. Selling high-end tech products to companies isn’t the same as selling dresses to regular people, but both are important.
Sound interesting? In this blog, we’ll talk about the sales concept in general, 10 different types of sales, top strategies, and common sales-related terms for your better understanding.
What is Sales?
Sales typically refer to the exchange of goods, services, or other property for money or other forms of compensation.
It’s a key part of how businesses operate, where products or services are marketed and sold to customers. The process includes various activities performed by a company both to make a sale and also involves different parties such as:
- Buyer: The person who is planning to purchase.
- Seller: The person or company offering the product or service for sale.
- Product/Service: What is being sold, bringing the buyer and seller together.
- Sales Process: The series of actions and steps taken by a business to facilitate a sale.
Sales Vs Marketing
Sales and marketing these two are very closely related but both have distinct functions within a business. They each play a critical role in driving company revenue and promoting growth. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
Objectives
- Sales: It aims to generate revenue by converting leads into paying customers through personal interactions, negotiations, and transactions.
- Marketing: Marketing focuses on creating awareness of your product offerings, generating interest, and facilitating the sales process by attracting potential customers, nurturing leads, and fostering brand loyalty.
Focus
- Sales: Focuses on one-on-one interactions with prospects and customers, identifying their requirements, addressing objections or pain points, and closing deals.
- Marketing: Focuses on understanding the target markets, developing strategies to reach and engage with potential customers, and creating proper messaging, and campaigns to drive interest and demand for the product offerings.
Activities
- Sales: Activities include prospecting, lead qualification, product demonstrations, negotiations, and closing deals.
- Marketing: Activities consist of market research, branding, advertising, content creation, social media engagement, email campaigns, SEO, lead nurturing, and many other things.
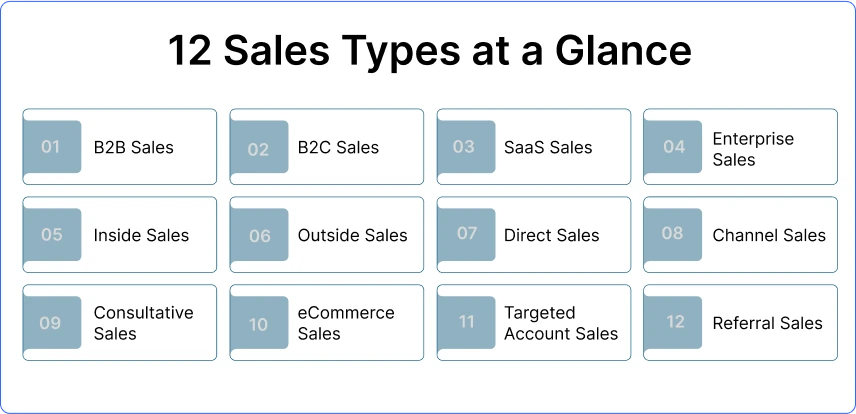
12 Different Types of Sales
For advising customers to sell things online and offline, everyone has their way of making deals. Confused? No worries. Sales is a broad topic, so let’s make it easier by looking at the different types of business sales and explaining each one clearly. Here’s a breakdown for you!
1. B2B Sales
B2B sales (business-to-business) refers to transactions or exchanges of products or services between two businesses rather than between a business and a consumer. In B2B sales, the customers are typically other businesses, institutions, or organizations, rather than individual consumers.
Such types of B2B sales are often more complicated, with more people involved, and they usually take longer than selling directly to consumers like B2C sales.
B2B sales usually fall into three main categories:
- Wholesale/Distribution Sales: This involves selling raw materials or products in bulk to other businesses. For instance, a corner shop might buy snacks and drinks in bulk from a wholesale supplier.
- Supply Sales: These are sales of items like office supplies and equipment to other businesses. Think of it as selling things a business needs to keep running smoothly.
- Service/Software Sales: This type involves providing services or software solutions to businesses to help them with their daily tasks. For example, a small company might subscribe to a software tool to manage their customer interactions.
The B2B sales team is often responsible for:
- Identifying potential clients and initiating contact with them.
- Checking if a lead can be a paying customer.
- Demonstrating the value proposition of the company’s products or services to potential clients.
- Negotiating terms, prices, and contracts with clients to finalize deals.
- Securing deals and finalizing contracts with clients.
- Providing after-sales services.
2. B2C Sales
In B2C sales businesses sell directly to the individual customers, not to any business organization. It’s just like when you buy something online or in a store. For instance, fashion brand Zara is directly selling their apparel or fashion accessories to their customers through online and offline stores.
The B2C sales team is often responsible for:
- Identifying and reaching out to potential customers through various channels such as cold calling, email marketing, social media engagement, etc.
- Showcasing the features and benefits of the products or services to potential customers.
- Understanding customers’ needs and preferences to recommend the most suitable products or services that meet their requirements.
- Maintaining relationships with existing customers to encourage repeat purchases, gather feedback, and address any concerns or issues they may have.
- Identifying opportunities to promote additional products or services to existing customers based on their previous purchases or needs.
- Gathering information about the latest market trends, competitor activities, and consumer preferences to adapt new sales strategies.
3. SAAS Sales
The worldwide Software as a Service (SaaS) market was worth $157 billion in 2020. This is more than twice the value it had in 2015 and almost twelve times more than in 2010. And it’s not stopping there. Experts predict that in 2026 the SaaS market will grow even bigger, reaching $307 billion. So, there’s a huge amount of SaaS sales happening!
But what is SAAS sales? This type of sales involves selling Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions to businesses or individuals. Here companies provide software applications hosted on the cloud, accessible online through the internet on a subscription basis.
The SAAS sales team is often responsible for:
- Identifying potential customers who may benefit from their SaaS product through various channels like cold calling, email outreach, social media, etc.
- Evaluating leads to determine if they fit the target customer profile and have a genuine need for the SaaS solution.
- Conducting demonstrations or providing access to trial versions of the software to showcase its features and benefits.
- Understanding customer pain points and demonstrating how the SaaS product can address those effectively.
- Negotiating subscription terms, including pricing, contract duration, and any customization or additional services required by the customer.
4. Enterprise Sales
Enterprise sales, also referred to as complex sales is a type of B2B sales. It involves selling products or services to large organizations, ranging from mid-sized businesses to multinational corporations. These sales require dealing with big contracts, multiple decision-makers, higher risks, and longer sales cycles compared to other types of sales. To get success in enterprise sales you need to have a strategic approach, strong relationship-building skills, and a deep understanding of the customer’s business challenges and objectives.
The enterprise sales team is often responsible for:
- Identifying potential clients and opportunities within large corporations or organizations.
- Establishing and nurturing long-term relationships with key stakeholders and decision-makers within the target companies.
- Conducting thorough needs assessments to understand the specific challenges, goals, and pain points of potential clients.
- Creating and delivering personalized presentations and proposals that demonstrate how the company’s products or services can address the client’s needs and deliver value.
- Negotiating terms, pricing, and contracts for closing deals.
5. Inside Sales
Inside sales is frequently embraced in industries where products or services can be efficiently sold without requiring physical demonstrations or in-person visits. Essentially, this approach involves selling from within the company itself. Companies employing inside sales often have several automated procedures and organized schedules. Sales in this context revolve around selling to customers remotely, often through different channels like live chat, video conferencing, email, or telephone calls.
The Inside sales team is often responsible for:
- Initiating contact with potential customers and qualifying leads through outbound calls, emails, or online inquiries.
- Conducting product demonstrations or presentations remotely to showcase features, benefits, and USPs of their products.
- Providing information, answering questions, and addressing customer concerns to guide them through the purchase process.
- Negotiating terms, handling objections, and finalizing sales agreements without meeting customers in person.
- Assisting existing customers with post-sales inquiries, order tracking, and issue resolution through phone or online channels.
6. Outside Sales
Outside sales refers to the practice of making sales in person, typically by meeting clients at their location or in a face-to-face setting outside of a traditional office environment. In this sales approach, the team is usually trained on specific products, enabling them to guide prospects through all of its features and advantages.
The outside sales team is often responsible for:
- Prospecting, networking, and identifying potential customers or clients.
- They are responsible for converting leads into sales.
- They need to have a deep understanding of the products or services they are selling to effectively communicate their benefits to potential clients.
- Being up-to-date with industry trends, latest technologies, competitor activities, and market conditions.
- Outside sales reps often spend a significant amount of time traveling to meet with clients, attend trade shows, and participate in networking events.
7. Direct Sales
Direct sales is a process of selling things directly to customers without using a regular store. Companies usually rely on independent salespeople who sell things directly to customers by talking to them face-to-face, showing them products at home, at networking parties, or meeting them personally.
You can find direct sales in different industries like cosmetics, skincare, health products, kitchen items, and home goods. It’s a good way for companies to sell things directly to customers without spending too much money. And for the salespeople, it’s a great chance to earn incentives by selling products using their business skills.
Direct sales refers to two different ways sellers operate independently:
- Single-Level Marketing: It’s a straightforward approach where sellers focus on selling products directly to consumers without building multi-level teams or networks. A direct seller earns by purchasing products from a parent company and then selling them to their customers.
- Multi-level marketing (MLM): MLM involves sellers earning profits not only from their sales but also from the sales made by the individuals they recruit into their downline. The commission structure often incorporates bonuses and rewards for team-building and leadership.
The direct sales team is often responsible for:
- They often identify potential customers or prospects through various methods like cold calling, networking, or lead generation campaigns.
- Presenting products to potential customers, highlighting features, benefits, and USPs.
- They work to convert leads into customers by closing deals and finalizing sales transactions.
- Direct sales teams may also provide ongoing support to customers, addressing any issues or concerns they have after the sale.
- Understanding market trends, customer needs, and competitors’ strategies is often part of their role to adapt sales tactics accordingly.
8. Channel Sales
In channel sales, companies sell their products or services through other intermediaries, known as partners. This method is also referred to as partner selling or indirect selling because the company doesn’t deal directly with its customers. Instead, they rely on third-party partners such as resellers, distributors, or agents to reach a broader market. Distribution agreements establish guidelines for pricing, discounts, and customer service standards among these partners.
The channel sales team is often responsible for:
- Developing and maintaining relationships with channel partners to ensure effective collaboration and alignment with the company’s sales objectives.
- Identifying potential channel partners, evaluating their suitability, and onboarding them into the company’s channel program.
- Providing training and support to channel partners to ensure they have the necessary knowledge and resources to effectively sell the company’s products or services.
- Coordinating marketing and promotional activities with channel partners to generate demand and drive sales.
9. Consultative Sales
Consultative sales is all about shifting the focus from transactional selling to relationship-building and problem-solving. It is an approach to selling that first focuses on understanding the customer’s needs and then provides personalized solutions to address those requirements.
Instead of simply pitching products or services, consultative sales professionals act as trusted advisors to their customers, guiding them through the buying process and helping them make informed decisions.
The consultative sales team is often responsible for:
- Listening attentively to customers to uncover their underlying needs, preferences, and concerns.
- Using the insights gained to recommend customized solutions that address the customer’s specific needs.
- Working closely with product development, marketing, and customer support teams to ensure alignment between customer needs and company offerings.
- Guiding customers through the sales process from initial contact to price negotiation and closing.
- Continuing to engage with customers even after the sale to ensure satisfaction, address any issues or concerns, and identify opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
10. eCommerce Sales
E-commerce sales happen in two main ways: B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-consumer). Both involve selling items online, but they operate differently.
In B2C sales, it’s just like when you shop online. You might chat with someone to get instant assistance and then make a purchase quickly. On the other side, B2B sales involve businesses selling to other businesses online. This often includes more complex processes like demonstrating products to generate interest.
Regardless of whether it’s B2B or B2C, it all revolves around buying and selling electronically, usually through a website or app.
The eCommerce sales team is often responsible for:
- Finding and acquiring new customers through various online channels such as search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, social media marketing, email marketing, etc.
- They work on strategies to retain existing customers by ensuring a positive shopping experience, implementing loyalty programs, and engaging in personalized marketing efforts.
- Developing and implementing sales strategies tailored to the company’s eCommerce platform, target audience, and product offerings.
- They are responsible for presenting products effectively on the company’s eCommerce website, including product descriptions, images, and videos.
- They handle the process of order fulfillment, ensuring that orders are processed efficiently and accurately.
11. Targeted Account Sales
In this type of sales, the team concentrates on particular groups of customers. They make customized plans for each customer. Sales and marketing work together to adjust messages and deals to fit each customer’s requirements. This approach helps salespeople build relationships with customers over time, which leads to more sales in the long run.
The targeted account sales team is often responsible for:
- They research and identify high-potential accounts that align with the company’s strategic goals and offerings.
- They go through the challenges, objectives, and preferences of each target account to tailor their approach accordingly.
- They collaborate closely with the marketing team to align messaging, content, and campaigns with the targeted accounts’ interests and pain points.
- They establish relationships with key decision-makers and influencers within the target accounts through various channels, such as meetings, calls, emails, and social media.
12. Referral Sales
Referral sales, also known as word-of-mouth sales, is a strategy where businesses encourage their existing customers to recommend their products or services to others. You can encourage your current customers to bring in new potential leads by providing incentives, special discounts, or gift vouchers.
The referral sales team is often responsible for:
- They create and manage different referral programs.
- They educate existing customers about the referral program, its benefits, and how they can participate effectively.
- They monitor and track the referral activities, including the number of referrals generated, the quality of leads, and the conversion rates from referrals to customers.
Top 10 Effective Sales Methodologies
Remember, you don’t have to begin from square one with every lead. Instead, many companies rely on different sales methodologies as structured frameworks to guide consumers through the different stages of deals. Here are some of the primary sales methodology examples commonly utilized by various companies.
- Solution Selling: solution selling emphasizes understanding the customer’s pain points and offering solutions that address those specific needs.
- Inbound Selling: This involves attracting potential customers through content marketing, social media, and other channels, nurturing those leads through the sales funnel, and providing helpful information throughout the buying process.
- SPIN Selling: SPIN stands for the four kinds of questions salespeople should ask their clients: Situation, Problem, Implication, and Need-Payoff. Answers to these questions give info on what’s bothering the clients and help the salesperson connect better with them.
- N.E.A.T. Selling: This is a way to decide if a lead is worth pursuing. N.E.A.T. stands for what the customer needs, economic impact, who are the decision-makers, and if there’s a good reason to buy now.
- Conceptual Selling: This method helps the salespeople to understand what customers think about their product offerings and how they make the final buying decision.
- SNAP Selling: It’s an abbreviation for: keep it simple, be invaluable, ensure alignment, and prioritize needs.
- The Challenger Sale: It emphasizes the salesperson’s ability to question the customer’s mindset, which includes educating them, tailoring insights to their needs, and steering the sales process.
- The Sandler System: It focuses on creating trust between the salesperson and the potential customer. The salesperson acts like a guide and asks questions to understand the problems and pain points of the potential customer.
- Customer-Centric Selling: Here the salesperson talks to the main decision-makers of the company who will buy the products and figures out ways to solve the problems or challenges they’re dealing with.
- MEDDIC: The acronym stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, and Champion. This involves identifying what success looks like for the prospect and how the product or service can contribute to achieving those goals.
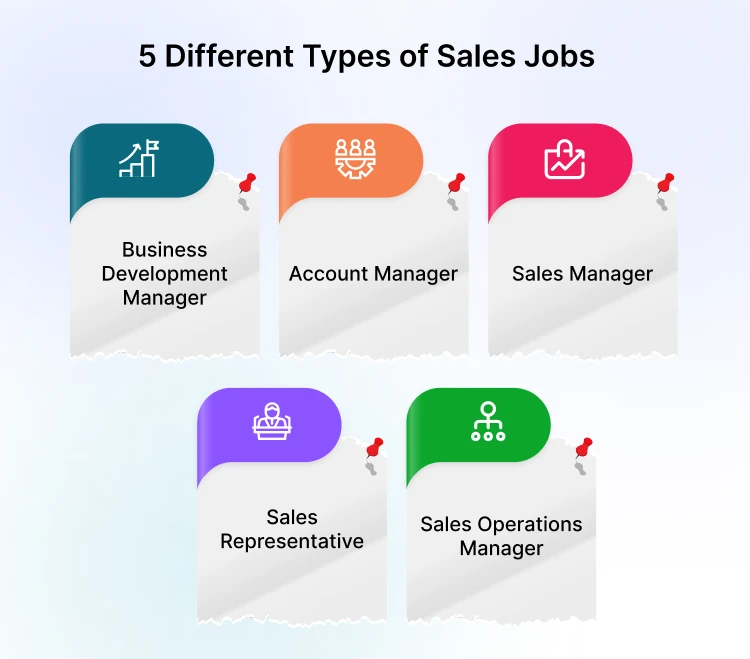
5 Different Types of Salespeople
As we have discussed the various ways of business sales and types of sales strategies, let’s check out the different sales positions. These people can work in many other segments and focus on different parts of the sales process. While there are more than the five types I’ve mentioned, this overview offers a solid starting point for you to understand key positions within the sales system.
1. Business Development Manager
Business development managers find new chances for the company to grow. They are responsible for searching potential customers, setting up meetings with them, and discovering new opportunities. They work with all the important departments of the company to understand target clients, markets, products, and sales better.
Key qualities for business development managers:
- Good communicator
- Friendly and empathetic
- Good at making connections
- Great at solving problems
- Team player
- Honesty and trustworthy
2. Account Manager
Account managers are responsible for managing relationships with key clients or accounts. They serve as the main point of contact for those clients, address their needs and pain points, and work hard to grow revenue by upselling or cross-selling additional products or services.
Key qualities for account managers:
- Strong communication skills
- Excellent relationship building
- Customer-centric approach
- Strategic thinking
- Negotiation skills
- Problem-solving abilities
3. Sales Manager
Sales managers are in charge of the teams of salespeople. Their job is to set clear goals for sales, come up with strategic plans, teach and help their team members, and check how well everyone is doing to make sure they meet their goals.
Key qualities for sales managers:
- Leadership Excellence
- Exceptional communication skills
- Goal-directed Approach
- Adaptive nature
- Problem-solving abilities
4. Sales Representative
Sales representatives are like the friendly face of the company. They’re the ones customers usually meet and talk to. Their main job is to sell the company’s products to their customers. They usually work in a specific area or with certain types of customers. Their goal is to bring in new business and make sure current customers are happy.
Key qualities for sales representatives:
- Good communicator
- Friendly and approachable
- Knowledgeable
- Problem solver
- Self-Motivated
- Honest and trustworthy
5. Sales Operations Manager
Sales operations managers ensure that the sales process runs smoothly and help the sales team work better. They might help predict sales, plan territories, analyze sales data, manage CRM systems, and find ways to make the sales process work better.
Key Qualities for Sales Operations Managers:
- Analytical skills
- Problem-solving abilities
- Attention to detail
- Strategic thinking
- Good communication skills
- Technical proficiency
- Leadership skills
Some Common Sales Terms to Know
- Lead: A lead is someone or a company that has shown interest in what another company offers. They could end up becoming a customer in the future.
- Prospect: A potential customer who might be interested in what your company is selling.
- Sales Funnel: A sales funnel is like a path that a potential buyer follows from first knowing about a product, to being interested, deciding to buy it, and finally making the purchase.
- Conversion: It refers to the moment when a potential customer takes a desired action, such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a signup form.
- Salesperson: A salesperson is someone who sells products, services, or ideas of a company to potential customers or clients.
- Deal: This term typically refers to an agreement or transaction between a seller and a buyer.
- Full Funnel Strategy: A full-funnel strategy is just like a comprehensive roadmap that starts with making your target people aware of your brand and then guides them through a customer journey designed to convince them to purchase from you.
Manage Your Sales with REVE Chat
No matter how you define sales, salespeople dedicate considerable time and effort to building connections and nurturing relationships. Customers expect personal engagements and seek tailored information and services. Just like customer service, maintaining a strong rapport with customers is essential for the sales team.
To enhance customer relationships and boost online sales, consider using REVE Chat. It’s a customer engagement platform designed to provide instant assistance across various online platforms such as web, mobile, Facebook, Instagram, Telegram, Viber, and WhatsApp.
With REVE Chat, you can monitor website and mobile app visitors in real time and reach out to them proactively to offer immediate assistance and personalized services. Additionally, REVE Chat offers an AI-powered Chatbot to automate many business operations, including customer service.
Interested in trying it out? SIGN UP for a 14-day free trial today.