Digital Banking in Bangladesh: A Begining of a New Era
- November 8, 2023
- 18 mins read
- Listen

Table of Content
Bangladesh is surging ahead in the finance realm to embrace digital banking at an astounding pace. Just think of a place for a minute where banking is as effortless as a text message. You can access savings, make payments, and invest, all with a few taps on your smartphone.
Bangladesh aims for 75% of local transactions to go digital by 2027, as a vision of a “Smart Bangladesh” by 2041. Notably, Nagad Digital Bank and Kori Digital have recently joined as newly licensed digital banks to start a new beginning.
In this blog, we are going to explore the whole scenario of digital banking in Bangladesh, its transformation, types, comparison with traditional banking, and many more. So, if you want to stay updated about this FinTech revolution in Bangladesh then keep reading this blog.
What is Digital Banking?
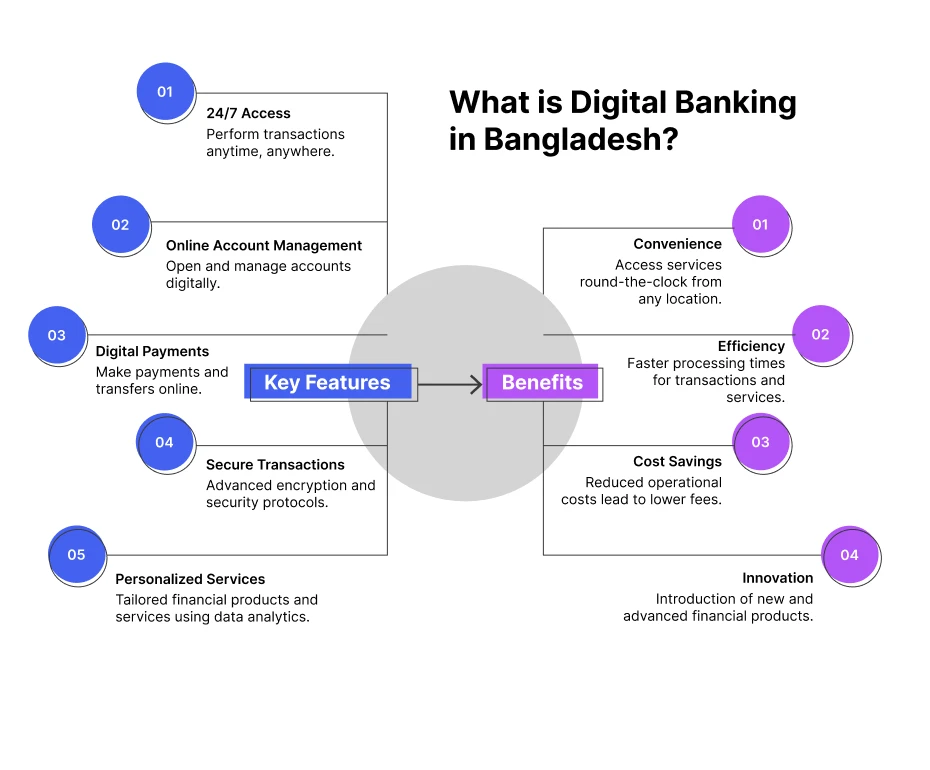
Digital banking refers to the use of digital technology and online channels to provide a wide range of financial services to customers. Unlike traditional banking, digital banking operates in a branchless and virtual environment. The primary objective of digital banking is to enhance accessibility, convenience, and efficiency for users. It eliminates the need for physical branches and allows transactions and interactions through electronic means.
Additionally, digital banking has further evolved with the emergence of Neo-Banking. Neo-banks, or digital-only banks, operate exclusively online without physical branches. They leverage technology to provide innovative and user-centric financial solutions. The integration of Neo-Banking concepts aligns with the broader trend of using technology to transcend geographical limitations and time constraints to the evolving needs of a digitally connected society.
In digital banking, customers can access their accounts, conduct transactions, and manage their finances through secure online interfaces. Furthermore, it facilitates electronic payments and transfers that reduce reliance on physical currency. It often incorporates advanced security measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring to ensure the safety of customer information and prevent unauthorized access.
Banking Transformation Over Time in Bangladesh
The banking sector in Bangladesh has undergone significant transformations over the years. They are evolving from traditional banking methods to the modern, digital banking landscape we see today. This transformation has been driven by technological advancements, regulatory reforms, and a growing demand for financial inclusion.
The turn of the 21st century marked a significant shift in Bangladesh’s banking sector with the introduction of technology-driven solutions. The advent of core banking systems, automated teller machines (ATMs), and electronic fund transfers revolutionized how banking services were delivered. These innovations increased efficiency, reduced transaction times, and enhanced customer convenience.
In recent years, the rise of mobile banking and internet banking has further transformed the landscape. Mobile financial services (MFS) like bKash and Nagad have gained widespread popularity. They are offering banking services to millions of unbanked and underbanked individuals. These services have played a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion and bringing banking facilities to rural and remote areas.
In a bid to modernize the financial sector and reduce the economy’s reliance on cash, Bangladesh Bank has been proactive in issuing licenses for digital banks. These institutions operate primarily online, providing a range of banking services without the need for physical branches.
In recent developments, Bangladesh Bank approved the establishment of two new digital banks, and plans are underway to issue more licenses. This move aligns with the government’s vision of a cashless society and reflects the growing acceptance of digital financial solutions among the population.
The regulatory environment has been a key enabler of the banking sector’s transformation. Bangladesh Bank has introduced various guidelines and frameworks to support digital banking initiatives. These regulations ensure the security, efficiency, and transparency of digital transactions.
Different Types of Digital Banking in Bangladesh
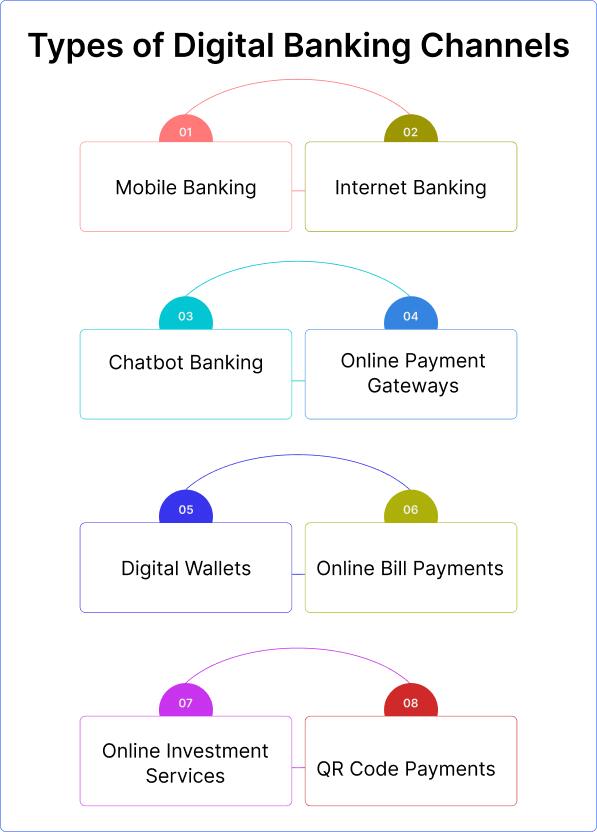
1. Mobile Banking
It allows customers to access their bank accounts and conduct financial transactions using a mobile device, typically through a dedicated banking app or mobile web browser. It offers features like checking balances, transferring funds, bill payments, and mobile deposits.
2. Internet Banking
It also known as online banking enables customers to access their bank accounts and perform transactions through a web portal using a desktop or laptop computer. It provides services such as account management, bill payments, and fund transfers.
3. Chatbot Banking
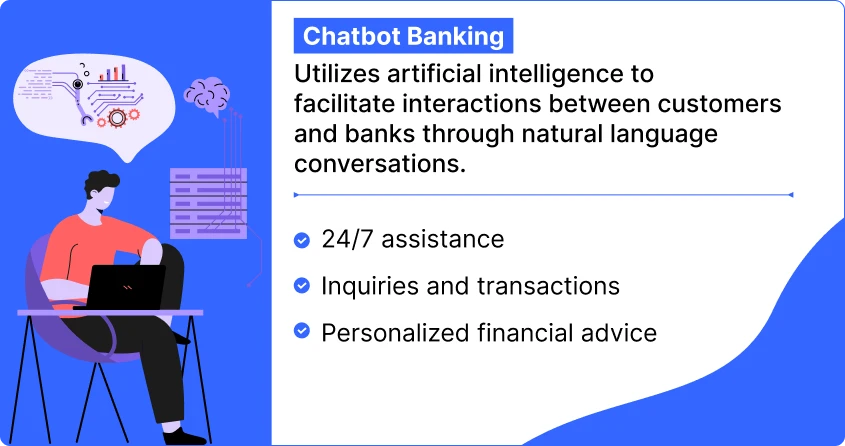
Chatbot banking brings convenience and accessibility to the financial landscape. This innovative technology employs artificial intelligence to enable meaningful interactions between customers and their banks through natural language conversations.
It simplifies financial tasks, offering 24/7 assistance for inquiries, transactions, and personalized financial advice, all via a chat interface. Chatbot is revolutionizing traditional banking by providing instant, personalized support and fostering a more intuitive and user-friendly banking environment. For example, the Bank of Kuwait uses REVE Chat to provide superfast customer support with ease.
4. Online Payment Gateways
These gateways are digital platforms that facilitate secure online transactions. They are commonly used for e-commerce and allow customers to make purchases or payments electronically.
5. Digital Wallets
It is also known as e-wallets are mobile apps or online platforms that allow users to store and manage their payment information, such as credit card details and bank account information. They enable quick and secure payments for a wide range of transactions, both online and in physical stores.
6. Online Bill Payments
Online fund transfer services allow users to send money to individuals or businesses electronically. These services include peer-to-peer (P2P) payment platforms, wire transfers, and interbank transfers. They offer a convenient and efficient way to move money between accounts.
7. Online Investment Services
It also known as robo-advisors or online brokerage platforms, provides individuals with the ability to invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other financial instruments online. They often use algorithms to offer investment advice and portfolio management services.
8. QR Code Payments
It involves scanning a Quick Response (QR) code with a mobile device to initiate a payment. This technology is commonly used for in-store and person-to-person (P2P) transactions, making payments swift and contactless.
Digital Banking Vs Online Banking Vs Mobile Banking
Various banking services are available to meet the diverse needs of consumers. It is pivotal to understand the key distinctions between digital banking, online banking, and mobile banking. Knowing the main difference is crucial for navigating these services effectively.
Here’s a breakdown of each:
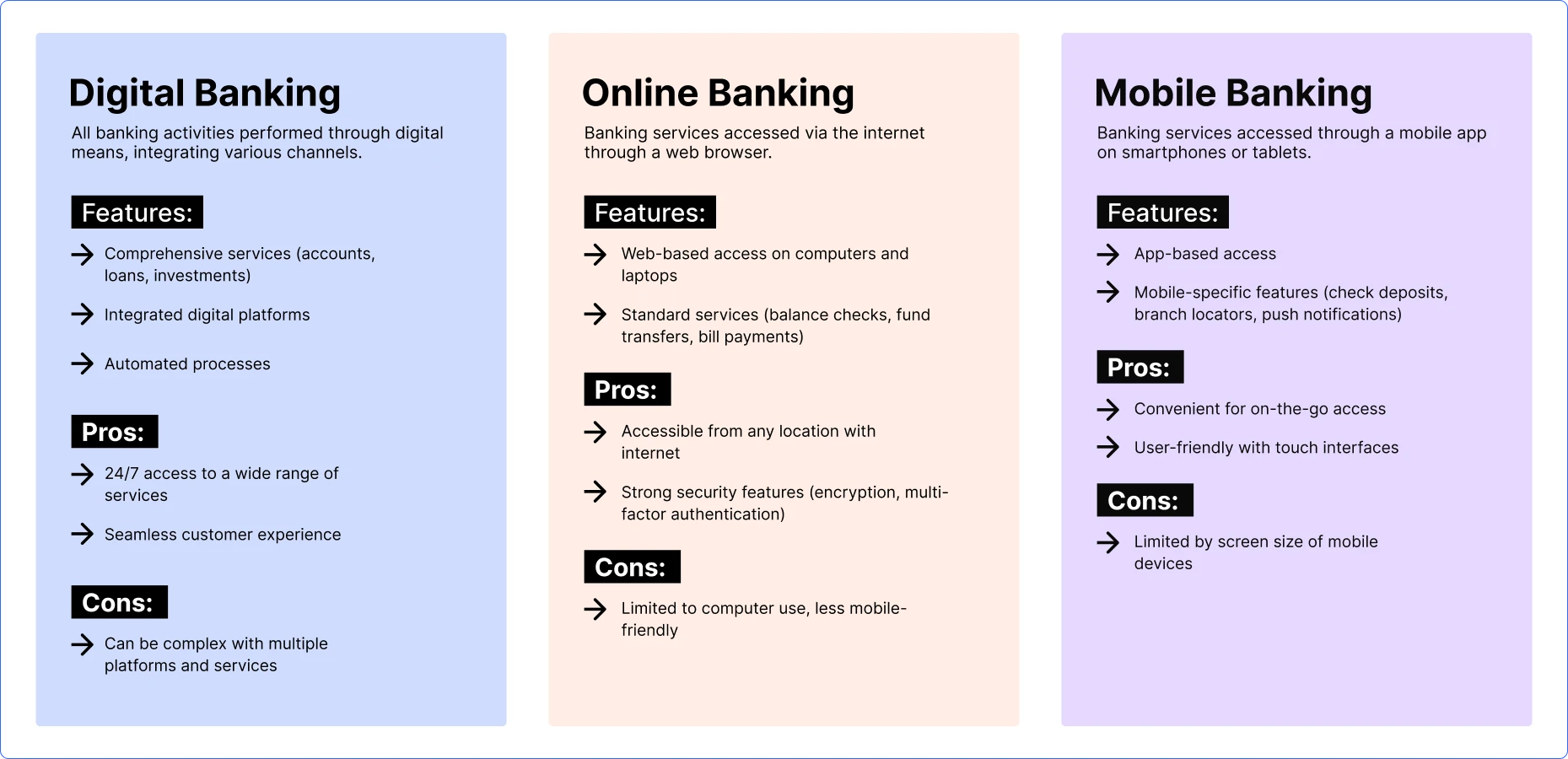
1. Digital Banking
Digital banking encompasses all forms of banking activities performed through digital means. It includes not only online and mobile banking but also other digital channels like automated kiosks and self-service terminals.
- Comprehensive Services: Digital banking offers a full range of banking services, from account management to loans and investments, accessible through multiple digital platforms.
- Integration: It integrates various banking channels into a unified digital experience, providing a seamless customer journey.
- Automation: Digital banking often involves automated processes for tasks like fund transfers, account updates, and customer support, enhancing efficiency.
Pros
- Access to banking services anytime and anywhere, beyond traditional banking hours.
- Users can manage all aspects of their banking needs through a single digital platform.
Cons
- The range of services and platforms can sometimes be overwhelming or confusing for users.
2. Online Banking
Online banking refers specifically to banking services accessed via the Internet through a web browser on a computer or laptop. It is a subset of digital banking.
- Web-Based Access: Users access their bank accounts and perform transactions through a bank’s website.
- Standard Services: Includes account balance checks, fund transfers, bill payments, and transaction history.
Pros
- Offers access to banking services from any location with an internet connection.
- Online banking platforms typically have robust security measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Cons
- It may not be as convenient for users on the go.
3. Mobile Banking
Mobile banking involves accessing banking services through a mobile application installed on a smartphone or tablet. It is a specific form of online banking optimized for mobile devices.
- App-Based Access: Users perform banking activities through a dedicated mobile app.
- Mobile-Specific Features: Often includes features like mobile check deposit, GPS-based branch locators, and push notifications for account activity.
Pros
- Designed for users who need to manage their finances while traveling or away from their computers.
- Mobile apps are often optimized for ease of use with touch interfaces and quick access to frequently used features.
Cons
- Limited by the smaller screen size of mobile devices, which can impact the user experience for complex transactions.
What are the Challenges of Digital Banking in Bangladesh?
Balancing convenience with concerns about security and technological accessibility can be a big challenge for the customer. On the flip side, navigating cybersecurity risks, regulatory compliance, and integrating digital innovations within existing systems pose hurdles for banks embracing digital transformations.
Let’s take a deep look at the key challenges customers and banks may encounter.
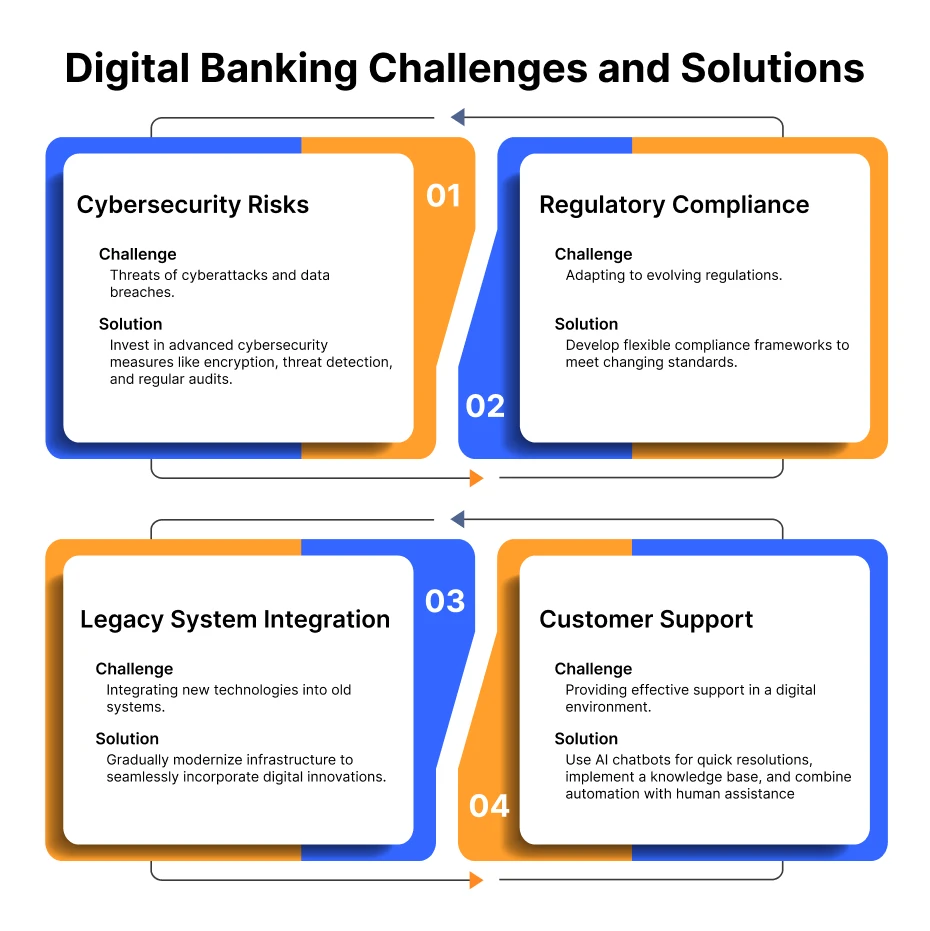
1. Cybersecurity Risks: Banks encounter escalating threats of cyberattacks and data breaches. Banks must ensure robust security measures and ongoing investments in cybersecurity infrastructure.
Solution:
- Investment in Cybersecurity: Continual investment in advanced cybersecurity measures, including encryption technologies, threat detection systems, and regular security audits to safeguard against cyber threats.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to ever-evolving regulations and compliance standards in various jurisdictions poses a challenge. It requires continual adaptation and resources.
Solution:
- Adaptive Compliance Frameworks: Develop flexible and adaptive compliance strategies to navigate changing regulatory landscapes and ensure adherence to evolving standards.
3. Legacy System Integration: Introducing digital innovations into existing legacy systems can be complex and costly. It hinders the seamless integration of new technologies.
Solution:
- Modernizing Infrastructure: Gradually modernizing legacy systems to enable integration of digital innovations. It ensures they complement and enhance existing banking operations rather than disrupt them.
4. Customer Support: Offering effective customer support can be a big challenge in digital banking. It involves addressing the demands for automated query resolution, timely responsiveness, and maintaining a human touch in a virtual environment.
Solution:
- Chatbot: Using AI-powered Chatbots for quick query resolution, implementing a well-structured knowledge base, and combining automation with personalized human assistance can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of customer support in digital banking.
Digital Banking Trends in Bangladesh
Several trends are shaping the landscape of digital banking in Bangladesh. It’s important to note that the digital banking industry is dynamic, and new trends may have emerged since then.
Now let’s explore the digital banking trends in Bangladesh.

Here are some of the current trends in digital banking up to that point:
1. Open Banking and API Integration
Open banking initiatives, such as PSD2 in Europe, have promoted data sharing between banks and third-party providers through APIs. This enables customers to access a broader range of financial services and manage multiple accounts from a single platform.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Banks are using AI and machine learning for enhanced customer service, personalized product recommendations, fraud detection, and credit risk assessment. Chatbots and virtual assistants have become common in customer support.
3. Biometric Authentication
Enhanced security measures, such as biometric authentication (fingerprint, facial recognition, and voice recognition), are increasingly used for secure access to mobile banking apps and online accounts.
4. Contactless Payments
The adoption of contactless payment methods, including mobile wallets (Apple Pay, Google Pay) and contactless cards, has grown significantly, especially in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
5. Cryptocurrency Integration
Some banks are exploring or integrating cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, offering services like cryptocurrency custody and trading to meet the evolving demands of customers.
6. Robo-advisors and Wealth Management
It continues to gain traction, providing automated and algorithm-based investment advice to customers. These platforms make investing more accessible and affordable.
7. Digital Identity Verification
Digital banks and financial institutions are investing in advanced digital identity verification methods to streamline the onboarding process and comply with regulatory requirements, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) checks.
8. Enhanced Cybersecurity
With the increased digital footprint, cybersecurity remains a top priority. Banks are adopting advanced security measures, such as multi-factor authentication and AI-driven threat detection, to protect customer data and assets.
9. Real-Time Payments
Real-time payment systems are being adopted in many countries, allowing instant fund transfers and reducing the time and cost associated with transactions.
10. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with evolving financial regulations, including data privacy laws like GDPR and consumer protection regulations, is a significant focus for digital banks.
Key Benefits and Impacts of Digital Banking for Bangladesh
Digital banking in Bangladesh is going to change the entire scenario of the FinTech industry. However, how the customer and banks receive the benefits. Let’s find the answer below.

Customer Benefits
What benefits digital banking in Bangladesh will bring for the customers? How it will impact their finance management? Below are some benefits for customers.
- Convenience: Customers enjoy unparalleled convenience with 24/7 access to banking services from anywhere. It eliminates the need to visit physical branches. Transactions, account inquiries, and even financial advice are just a tap away on their smartphones or devices.
- Efficiency: Digital banks offer swift and seamless transactions. Tasks like fund transfers, bill payments, and account management take mere minutes. It reduces wait times and bureaucracy associated with traditional banking.
- Personalization: These banks often leverage data-driven insights to tailor services to individual customer needs. With personalized recommendations to targeted financial advice, customers experience a more customized and relevant banking experience.
- Lower Costs: Digital banks typically have fewer overhead expenses related to maintaining physical branches. As a result, they often offer lower fees, higher interest rates on savings, and better exchange rates, providing cost savings and better value to customers.
- Enhanced Security: Advanced security measures, such as biometric authentication and encryption technologies, ensure robust protection of customer data and transactions to foster trust and confidence among users.
Bank Benefits
Below are some common benefits banks will get in a digital baking setting.
- Scalability: Digital banks have the advantage of rapid scalability, as their operations are not tied to physical infrastructure. They can expand their services and customer base swiftly and cost-effectively to tap into a broader market without the constraints of brick-and-mortar limitations.
- Data Analytics: Access to vast amounts of data generated by customer interactions. They can leverage this data through analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends. This information helps in refining services to create targeted marketing campaigns, and making data-driven business decisions.
- Agility and Innovation: Digital banks operate in an environment that fosters innovation and agility. They can quickly adapt to market changes, integrate new technologies, and roll out innovative services to stay ahead of the curve in meeting evolving customer demands.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Without the overheads of maintaining physical branches, digital banks can significantly reduce operational costs. This includes expenses related to property, staffing, and infrastructure maintenance. It allows them to allocate resources more efficiently.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: It can reach underserved populations to provide banking services to those who have limited access to traditional banks. This inclusivity not only serves a societal purpose but also opens up new markets and revenue streams for the bank.
How is Bangladesh Adapting Digital Banking?

Bangladesh is undoubtedly making significant strides towards embracing digital banking. A total of 52 domestic and foreign entities have applied to the central bank for the license to set up digital banks. The Business Standard reports that the Bangladesh Bank made a decision to approve digital banking licenses to two of the 52 applicants, as confirmed by a senior official from the central bank.
The two newly licensed digital banks are Nagad Digital Bank and Kori Digital. The Bangladesh Bank has granted permission to three other applicants to establish digital banking services with the support of various traditional banks.
Furthermore, there are three more applicants, who have the backing of fintech firms and other companies, who may also be granted licenses after a thorough six-month evaluation period to assess the performance of the initial two digital banks.
However, the question of whether it is fully ready for this transformation involves several key considerations:
- Infrastructure: The readiness for digital banking in Bangladesh hinges on its technological infrastructure. While the country has seen an increase in mobile penetration and internet access, there is still room for improvement, especially in rural areas. A robust and widespread digital infrastructure is essential for the success of digital banking.
- Regulatory Framework: The regulatory framework plays a pivotal role in shaping the digital banking landscape. Bangladesh has recognized the importance of digital banking, and its regulators have taken initial steps to facilitate the integration of fintech and traditional banking. However, continued development and adaptation of regulations are necessary to ensure security, consumer protection, and innovation in the sector.
- Collaboration: Collaboration between traditional banks and fintech firms is often the key to successful digital banking. Bangladesh is seeing some collaboration efforts, but fostering a culture of cooperation and synergy between these entities will be essential for the digital banking ecosystem’s growth.
- Security Measures: The proliferation of digital banking also brings security risks. Ensuring robust security measures and cybersecurity protocols is paramount to gain consumer trust and prevent cyber threats. Bangladesh needs to invest in advanced security infrastructure to safeguard its digital banking system.
- Consumer Awareness: An essential aspect of readiness for digital banking is the level of awareness and trust among consumers. People need to be educated about the benefits, risks, and how to use digital banking services effectively. Building this awareness is an ongoing process.
- Fintech Ecosystem: The development and growth of the fintech ecosystem play a significant role in the readiness for digital banking. The country has shown promise with its mobile financial services (MFS) providers like Rocket and bKash. The expansion of such services and the entry of new fintech players will further contribute to the readiness of digital banking.
- Education and Training: To fully adapt digital banking, Bangladesh must invest in education and training programs for its workforce to ensure they have the necessary skills to operate and manage digital banking systems effectively.
- Regulatory Support: Regulatory bodies should continue to support and encourage innovation in the financial sector. They need to be agile and responsive to changes in the digital landscape.
Examples of Digital Banking in Bangladesh
As Bangladesh is transforming its journey towards digital banking, two MFS companies Kori Digital and Nagad have already obtained their licenses from central Bangladesh. Other banks and financial institutes will get the license gradually.
Below are two examples of digital banks in Bangladesh.
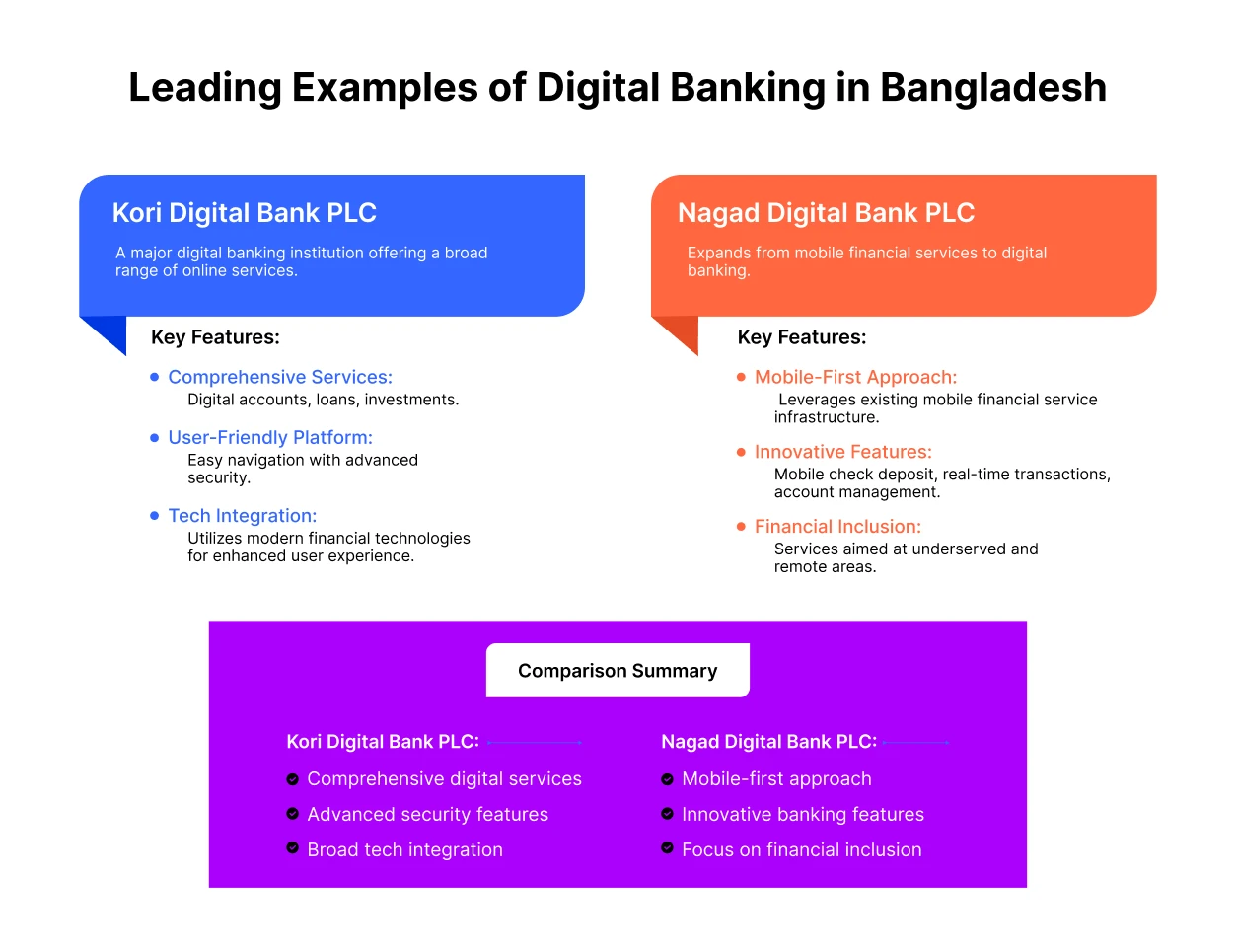
1. Kori Digital Bank PLC
Kori Digital Bank PLC is a prominent player in Bangladesh’s digital banking sector. They’re offering a full range of banking services through digital channels. It operates primarily online, providing customers with convenient access to account management, fund transfers, and other banking services.
Key Features
- Comprehensive digital services including loans and investments
- User-friendly online platform with advanced security features
- Integration with various financial technologies to enhance customer experience
2. Nagad Digital Bank PLC
Nagad, known for its mobile financial services, has expanded into digital banking with the launch of Nagad Digital Bank PLC. This digital bank offers a range of services designed to meet the needs of both individual and business customers.
Key Features
- Mobile-first approach, leveraging its existing mobile financial service infrastructure
- Features such as mobile check deposit, real-time transactions, and easy account management
- Focus on financial inclusion by providing accessible banking solutions to underserved areas
List of Banks That Are Moving to Digital Banking
There are 52 banks, that applied for digital banking licenses to the Bangladesh Bank. This list highlights 44 forward-thinking banks that have been at the forefront of this shift, actively embracing digital banking to offer their customers more convenient, efficient, and secure financial services.
As these institutions continue to evolve and adapt to the digital age, they are setting new standards and shaping the future of banking for the better.
- Alliance Fingular Islami Digi Bank PLC
- Nagad Digital Bank PLC
- bKash Digital Bank PLC
- Digi Ten PLC
- Digital Bank PLC
- Upay Digital Bank PLC
- JRF Digital Bank (BD) PLC
- Japan Bangla Digital Bank PLC
- Elegant Digital Bank PLC
- Digi Bank PLC
- North East Digital Bank PLC
- Next Century Digital Bank PLC
- Adhunik Bank PLC
- Somriddhi Digital Bank PLC
- Desh Digital Bank PLC
- Shonchoy Digital Bank PLC
- Smart Digital Bank PLC
- Shompod Digital Bank PLC
- North West Digital Bank PLC
- Bijoy Digital Bank PLC
- NUH Digital Bank PLC
- Uddipan Digital Bank Ltd
- UNO Digital Bank PLC
- Shomoy Digi Bank PLC
- Amar Digi Bank PLC
- Zamzam-Islami Digital Bank PLC
- Islami Digital Bank PLC
- Shuborno Digital Bank PLC
- Ekota Digital Bank PLC
- Sunam Digital Bank Ltd
- Bangladesh Digi Bank PLC
- Aalo Digi Bank PLC
- Aasha DigiBank PLC
- Delta DiGi Bank Ltd
- Starline Digital Bank PLC
- Shadin Digital Bank
- Sonali Bank
- Agrani Bank
- Janata Bank
- Rupali Bank
- Pathao Digital Bank PLC
- Agami Digital Bank PLC
- Artist Digi Bank PLC
- Shetu Digi Bank PLC
Conclusion
Digital banking isn’t just a trend; it’s a transformation that’s changing the way we interact with our money. From the palm of your hand, we can now manage your finances, invest, and make payments with unprecedented ease and security.
Frequently Asked Questions
Digital banking in Bangladesh refers to the use of digital technology to provide traditional banking services. This includes using online platforms, mobile applications, and other electronic channels to perform banking activities such as opening accounts, transferring funds, paying bills, and applying for loans.
Digital banks function primarily through digital means without the need for physical branches that help customers access banking services conveniently from anywhere at any time.
The advantages of digital banking are numerous. It offers unparalleled convenience that plays a key role for customers to access banking services 24/7 from any location with an internet connection.
Transactions and processing times are significantly faster compared to traditional banking, which enhances customer satisfaction. Digital banking is also cost-effective. It reduces operational costs for banks and often results in lower fees for customers.
Advanced encryption and security protocols ensure that user data and transactions are well-protected.
It brings several benefits, including promoting financial inclusion by providing banking access to underserved and rural areas.
This helps in integrating more people into the formal financial system, supporting economic growth through easier and quicker financial transactions. The adoption of digital banking encourages innovation in the financial sector. It results to the development of new financial technologies and services.
Moreover, it offers immense convenience to customers by allowing them to perform banking activities without the need to visit physical branches, saving them time and effort.
Digitization in banking offers significant advantages, including enhanced efficiency through automated operations and faster transaction processing. It broadens access to banking services. In particular for remote and rural populations, and leads to cost savings for banks, which can translate into lower fees for customers. Improved data collection and analysis enable better decision-making.
However, there are also disadvantages, such as security risks associated with potential cyberattacks and data breaches. The digital divide presents challenges for customers who are not tech-savvy or lack access to digital devices and the internet.
Additionally, overreliance on technology can be problematic during system outages, and handling sensitive customer data raises privacy concerns.
Digital banking offers a wide range of products, including online checking and savings accounts that customers can manage digitally. It provides digital payment solutions like online bill payments, peer-to-peer transfers, and mobile wallet services.
Customers can apply for loans and credit cards online, and engage in investment services through digital platforms for trading stocks, bonds, and other securities. Digital banking also offers various insurance products for customers with easy online access to health, life, and vehicle insurance.
Both have their own advantages. Online banking, is accessed through web browsers on computers. It offers a comprehensive range of services suitable for detailed account management. It is highly secure with features like encryption and multi-factor authentication. However, it is less convenient for users on the go.
Mobile banking, on the other hand, is accessed via mobile apps on smartphones and tablets. It makes it ideal for users who need to manage their finances while traveling. It includes additional features such as mobile check deposits and push notifications for a more convenient and user-friendly experience for mobile device users.
It is better because it provides round-the-clock access to banking services. It eliminates the need to visit physical branches. It offers enhanced efficiency with faster transaction processing and cost-effective operations, which can lead to lower fees for customers.
Digital banking brings innovation by enabling the introduction of new financial products and services that meet the specific needs of customers. The convenience of accessing banking services from anywhere at any time.
Physical banking involves visiting a bank branch to perform transactions, requiring face-to-face interaction with bank staff, and is limited to banking hours and physical locations.
In contrast, digital banking is conducted online or through mobile apps, without the need for a physical presence at a bank branch.
Digital banking offers 24/7 accessibility from anywhere with internet connectivity for a more convenient and efficient way to manage finances.
Digital banking in Bangladesh faces several challenges. Limited access to reliable internet in some regions hinders the widespread adoption of digital banking services. Low levels of digital literacy among certain population segments pose another significant challenge.
Security concerns, such as the risks of cyberattacks and data breaches, need to be addressed to build trust among users. Robust regulatory frameworks are required to govern digital banking operations effectively.
Additionally, insufficient technological infrastructure in rural and remote areas remains a significant barrier to the full implementation of digital banking.
The first digital bank in Bangladesh is Kori Digital Bank PLC, marking a significant step towards modernizing the country’s banking sector. This milestone reflects the nation’s commitment to embracing digital transformation and improving financial services through innovative technologies.
E-banking in Bangladesh includes various forms of electronic banking services. Internet banking allows customers to access their accounts and perform transactions through web browsers. Mobile banking offers similar services through mobile apps on smartphones and tablets.
ATM services provide automated teller machines for cash withdrawals, deposits, and other transactions. SMS banking enables customers to perform banking activities via text messages, while telebanking involves conducting transactions over the phone.
The first e-banking service in Bangladesh was introduced by Standard Chartered Bank, which launched Internet banking services to offer customers online access to their accounts. This pioneering initiative paved the way for the development and expansion of e-banking services in the country.



